
When this information is sent - bit after bit -, the called upon device executes the request and transmits it's data back - if required - to the board over the same line using the clock signal still generated by the Controller on SCL as timing.īecause the I2C protocol allows for each enabled device to have it's own unique address, and as both controller and peripheral devices to take turns communicating over a single line, it is possible for your Arduino board to communicate (in turn) with many devices, or other boards, while using just two pins of your microcontroller.
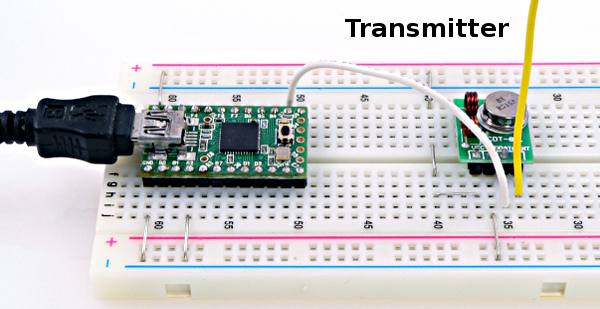
As the clock line changes from low to high (known as the rising edge of the clock pulse), a single bit of information - that will form in sequence the address of a specific device and a command or data - is transferred from the board to the I2C device over the SDA line. The I2C protocol involves using two lines to send and receive data: a serial clock pin (SCL) that the Arduino Controller board pulses at a regular interval, and a serial data pin (SDA) over which data is sent between the two devices. This article was revised on 8 by Karl Söderby.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
